CONTACT
TEL: +86-319-5986999
Phone:+86-15833709658
Email:602992806@qq.com
Address: No. 8 Simahuilong Street, Ningjin, Hebei
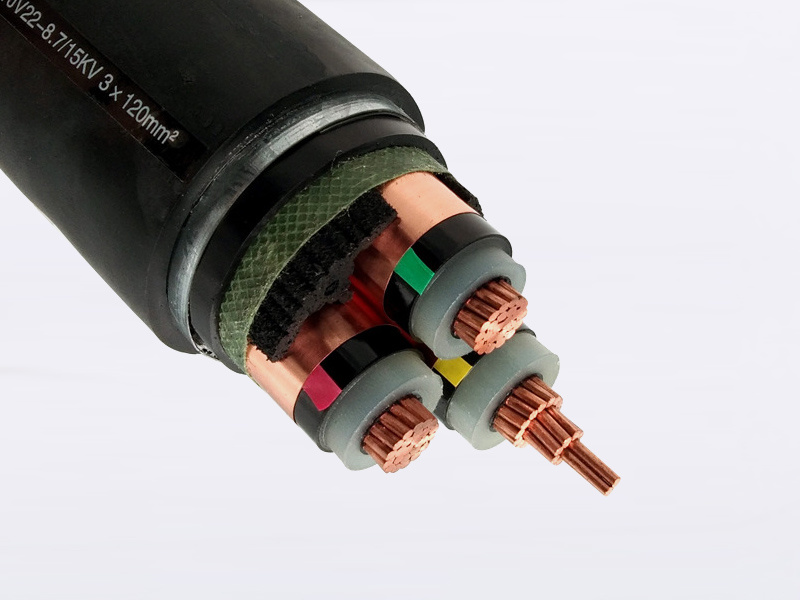
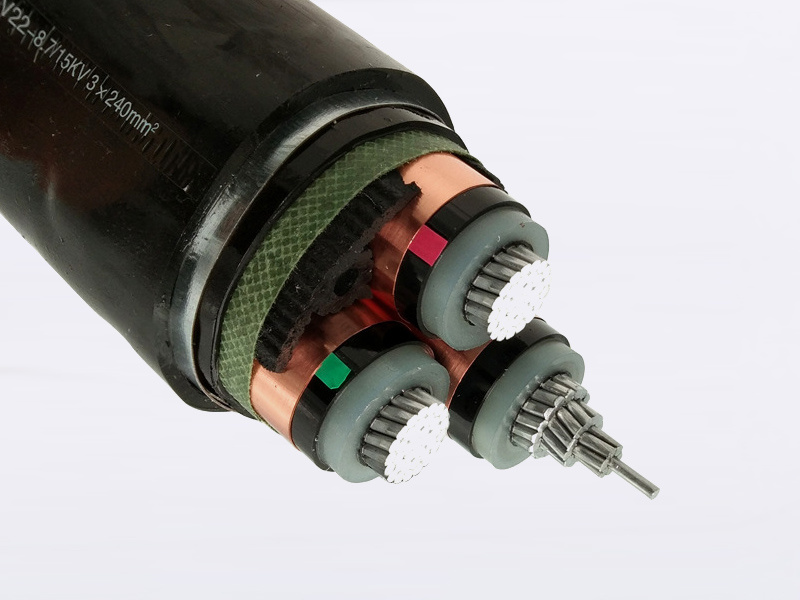
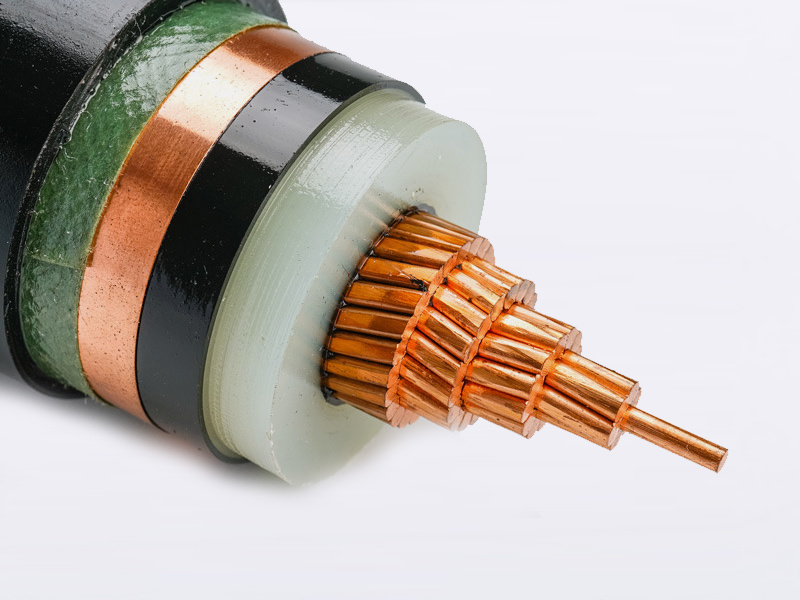
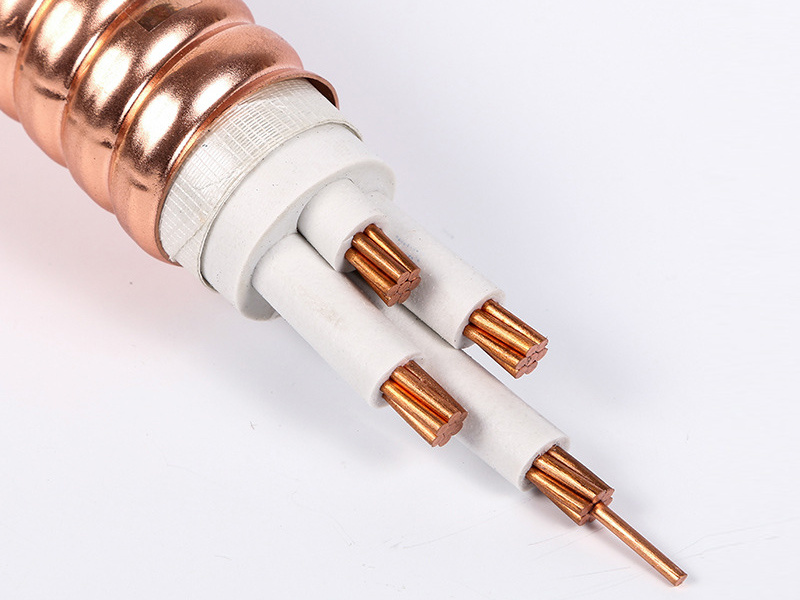
High-voltage power cable
- Product Description
-
Power cables are cables used for transmitting and distributing electrical energy. They are commonly employed in urban underground power grids, outgoing lines from power plants, and internal power supply systems within industrial and mining enterprises. As a key component of the main transmission lines in power systems, power cables are designed to efficiently carry and distribute high-power electricity across a wide range of voltage levels—ranging from 1 kV up to 500 kV and beyond—and come in various insulation types tailored to specific applications.
1. Product Name / Applicable Voltage
(0.6/1kV): Cross-linked Polyethylene Insulated Power Cable
Main raw materials: copper and aluminum conductors, cross-linked (XLPE) insulation, and PVC jacket
II. Product Execution Standards
The cable design complies with the requirements of the national standard GB/T12706-2008 and the International Electrotechnical Commission’s recommended standard IEC60502.
3. Product Applications
The conductor of cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables can operate at a normal temperature of 90°C. Not only do these cables boast excellent electrical performance, but they also feature high operating temperatures and large transmission capacities. Additionally, they offer advantages such as a simple structure, small outer diameter, lightweight design, ease of installation and use, and the ability to handle unrestricted installation height differences. As a result, they are widely used in industrial and mining enterprises as well as urban power grids.
4. Scope of Application
The application range of power cables includes installation indoors, outdoors, in conduits, cable trenches, and loose soil—environments that can withstand moderate pulling forces during installation but are not designed to endure direct mechanical stress. Additionally, single-core cables must not be installed in magnetic conduits.
V. Product Usage Characteristics
1. The ambient temperature during installation must not be lower than 0°C (if below 0°C, pre-heating is required); there are no restrictions on the cable's vertical drop.
2. The minimum bending radius requirements during installation are as follows: - For single-core non-armored cables: 20D; - For three-core non-armored cables: 15D; - For single-core armored cables: 15D; - For three-core armored cables: 12D; (Note: D refers to the actual outer diameter of the cable.)
3. Operating temperature of the cable: The PVC jacket should not exceed 90°C;
4. Overload Temperature: The maximum overload temperature for the cable during a short circuit is 130°C;
5. The maximum rated temperature of the cable conductor is 90°C, and during a short-circuit condition (lasting up to 5 seconds), the temperature does not exceed 25°C.
Contact us
TAG: